-
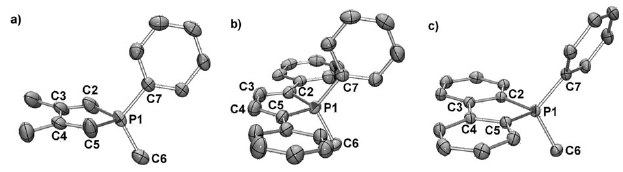
Synthesis of a stable radical anion via the one electron reduction of a 1,1-bis-phosphinosulfide alkene derivative

T. Cantat, F. Biaso, A. Momin, L. Ricard, M. Geoffroy, N. Mézailles and P. Le Floch
ChemComm, (7) (2008), p874-876


DOI:10.1039/b715380e | unige:42 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
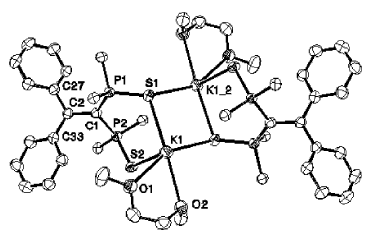
A new type of stable radical ligand featuring a 1,1-bis-phosphinosulfide alkene backbone has been prepared and characterized on the basis of X-ray diffraction, EPR and DFT studies.